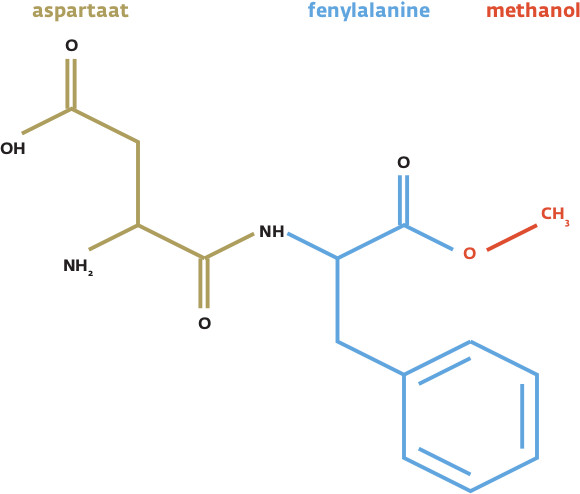
Rond aspartaam heeft altijd al een zweem van controverse gehangen. Ogenschijnlijk onterecht, want vanuit biochemisch standpunt lijkt aspartaam onschuldig. Toch zijn er vele redenen om die onschuld in twijfel te trekken. Over aspartaam blijft veel onenigheid bestaan, mede door mogelijke belangenverstrengeling in oud onderzoek en door recente studies die nieuwe effecten onthullen.
Beste bezoeker, u heeft geen toegang.
Enkel (web)abonnees hebben toegang tot tijdschriftartikelen. Het webabonnement is nog in de maak.
U kunt zich wel alvast (gratis) registreren en tal van andere webartikelen raadplegen!
Auteur
Verschenen in
Referenties
Kirkland D, Gatehouse D. Aspartame: A review of genotoxicity data. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015 Oct;84:161-8
EFSA. Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of aspartame (E 951) as a food additive. 2013 http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.2903/j.efsa.2013.3496/epdf
Halldorsson TI, Strøm M et al. Intake of artificially sweetened soft drinks and risk of preterm delivery: a prospective cohort study in 59,334 Danish pregnant women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010 Sep;92(3):626-33
Soffritti M, Belpoggi F et al. Aspartame administered in feed, beginning prenatally through life span, induces cancers of the liver and lung in male Swiss mice. Am J Ind Med. 2010 Dec;53(12):1197-206
Exposed: conflicts of interest among EFSA’s experts on food additives. Corporate Europe Observatory. 15 juni 2011 https://corporateeurope.org/sites/default/files/publications/efsa_ans_pa...
https://corporateeurope.org/sites/default/files/attachments/7-ans_food_a...
Belpoggi F, Soffritti M et al. Results of long-term carcinogenicity bioassay on Sprague-Dawley rats exposed to aspartame administered in feed. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Sep;1076:559-77
Soffritti M, Belpoggi F et al. Life-span exposure to low doses of aspartame beginning during prenatal life increases cancer effects in rats. Environ Health Perspect. 2007 Sep;115(9):1293-7
Soffritti M, Belpoggi F et al. First experimental demonstration of the multipotential carcinogenic effects of aspartame administered in the feed to Sprague-Dawley rats. Environ Health Perspect. 2006 Mar;114(3):379-85
Soffritti M, Belpoggi F, Degli Esposti D, Lambertini L. 2005. Aspartame induces lymphomas and leukaemias in rats. Eur J Oncol 10:107–116
Soffritti M, Padovani M et al. The carcinogenic effects of aspartame: The urgent need for regulatory re-evaluation. Am J Ind Med. 2014 Apr;57(4):383-97
National Toxicology Program. NTP report on the toxicology studies of aspartame (CAS No. 22839-47-0) in genetically modified (FVB Tg.AC hemizygous) and B6.129-Cdkn2atm1Rdp (N2) deficient mice and carcinogenicity studies of aspartame in genetically modified [B6.129-Trp53tm1Brd (N5) haploinsufficient] mice (feed studies). Natl Toxicol Program Genet Modif Model Rep. 2005 Oct;(1):1-222
Yılmaz S, Uçar A. A review of the genotoxic and carcinogenic effects of aspartame: does it safe or not? Cytotechnology. 2014 Dec;66(6):875-81. doi: 10.1007/s10616-013-9681-0. Epub 2014 Feb 8.
Kirkland D, Gatehouse D. Aspartame: A review of genotoxicity data. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015 Oct;84:161-8
Lim U, Subar AF et al. Consumption of aspartame-containing beverages and incidence of hematopoietic and brain malignancies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006 Sep;15(9):1654-9
Shindyapina AV, Petrunia IV et al. Dietary methanol regulates human gene activity. PLoS One. 2014 Jul 17;9(7):e102837
Španěl P, Dryahina K et al. Increase of methanol in exhaled breath quantified by SIFT-MS following aspartame ingestion. J Breath Res. 2015 Nov 19;9(4):047104
Trocho C, Pardo R et al. Formaldehyde derived from dietary aspartame binds to tissue components in vivo. Life Sci. 1998;63(5):337-49
Finamor I, Pérez S et al. Chronic aspartame intake causes changes in the trans-sulphuration pathway, glutathione depletion and liver damage in mice. Redox Biol. 2017 Apr;11:701-707
Maher TJ, Wurtman RJ. Possible neurologic effects of aspartame, a widely used food additive. Environ Health Perspect. 1987 Nov;75:53-7
Newman LC, Lipton RB. Migraine MLT-down: an unusual presentation of migraine in patients with aspartame-triggered headaches. Headache. 2001 Oct;41(9):899-901
Smith JD, Terpening CM et al. Relief of fibromyalgia symptoms following discontinuation of dietary excitotoxins. Ann Pharmacother. 2001 Jun;35(6):702-6
Burkhart CG. 'Lone' atrial fibrillation precipitated by monosodium glutamate and aspartame. Int J Cardiol. 2009 Nov 12;137(3):307-8
Robbins PI, Raymond L. Aspartame and symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome. J Occup Environ Med. 1999 Jun;41(6):418
Mortelmans LJ, Van Loo M et al. Seizures and hyponatremia after excessive intake of diet coke. Eur J Emerg Med. 2008 Feb;15(1):51
Yokogoshi H, Roberts CH, Caballero B, et al. Effects of aspartame and glucose administration on brain and plasma levels of large neutral amino acids and brain 5-hydroxyindoles[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 1984,40(1):1-7
Ashok I, Sheeladevi R, Wankhar D. Acute effect of aspartame-induced oxidative stress in Wistar albino rat brain. J Biomed Res. 2015 Sep;29(5):390-6
Adaramoye OA, Akanni OO. Effects of long-term administration of aspartame on biochemical indices, lipid profile and redox status of cellular system of male rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2016 Jan;27(1):29-37
Choudhary AK, Sheela Devi R. Longer period of oral administration of aspartame on cytokine response in Wistar albino rats. Endocrinol Nutr. 2015 Mar;62(3):114-22
Finamor I, Pérez S et al. Chronic aspartame intake causes changes in the trans-sulphuration pathway, glutathione depletion and liver damage in mice. Redox Biol. 2017 Apr;11:701-707
Feijó FM, Ballard CR et al. Saccharin and aspartame, compared with sucrose, induce greater weight gain in adult Wistar rats, at similar total caloric intake levels. Appetite. 2013 Jan;60(1):203-207
von Poser Toigo E, Huffell AP et al. Metabolic and feeding behavior alterations provoked by prenatal exposure to aspartame. Appetite. 2015 Apr;87:168-74
Choudhary AK. Aspartame: should individuals with Type II Diabetes be taking it? Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017 May 31. doi: 10.2174/1573399813666170601093336
Nettleton JE, Reimer RA, Shearer J. Reshaping the gut microbiota: Impact of low calorie sweeteners and the link to insulin resistance? Physiol Behav. 2016 Oct 1;164(Pt B):488-493
Swithers SE. Artificial sweeteners produce the counterintuitive effect of inducing metabolic derangements. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Sep;24(9):431-41
Suez J, Korem T et al. Artificial sweeteners induce glucose intolerance by altering the gut microbiota. Nature. 2014 Oct 9;514(7521):181-6
Palmnäs MS, Cowan TE et al. Low-dose aspartame consumption differentially affects gut microbiota-host metabolic interactions in the diet-induced obese rat. PLoS One. 2014 Oct 14;9(10):e109841
Gul SS, Hamilton AR et al. Inhibition of the gut enzyme intestinal alkaline phosphatase may explain how aspartame promotes glucose intolerance and obesity in mice. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2017 Jan;42(1):77-83
Humphries P, Pretorius E, Naudé H. Direct and indirect cellular effects of aspartame on the brain. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2008 Apr;62(4):451-62
Abu-Taweel GM, A ZM et al. Cognitive and biochemical effects of monosodium glutamate and aspartame, administered individually and in combination in male albino mice. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2014 Mar-Apr;42:60-7
Rycerz K, Jaworska-Adamu JE. Effects of aspartame metabolites on astrocytes and neurons. Folia Neuropathol. 2013;51(1):10-7
Konen JA, Sia TL et al. Perceived memory impairment in aspartame users. Presented at the Society for Neuroscience 30th Annual Meeting (2000, November), New Orleans, LA.
Sünram-Lea SI, Foster JK et al. Investigation into the significance of task difficulty and divided allocation of resources on the glucose memory facilitation effect. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2002 Apr;160(4):387-97
Harte CB, Kanarek RB. The effects of nicotine and sucrose on spatial memory and attention. Nutr Neurosci. 2004 Apr;7(2):121-5
Gendle MH, Smucker DM et al. Attention and reaction time in university students following the consumption of Red Bull. The Open Nutrition Journal. 2009; 3,8–10 doi: 10.2174/1874288200903010008
Sun-Edelstein C, Mauskop A. Foods and supplements in the management of migraine headaches. Clin J Pain. 2009 Jun;25(5):446-52
Jacob SE, Stechschulte S. Formaldehyde, aspartame, and migraines: a possible connection. Dermatitis. 2008 May-Jun;19(3):E10-1
Lindseth GN, Coolahan SE et al. Neurobehavioral effects of aspartame consumption. Res Nurs Health. 2014 Jun;37(3):185-93
Choudhary AK, Pretorius E. Revisiting the safety of aspartame. Nutr Rev. 2017 Sep 1;75(9):718-730
Choudhary AK. Aspartame: should individuals with Type II Diabetes be taking it? Curr Diabetes Rev. 2017 May 31. doi: 10.2174/1573399813666170601093336.
Choudhary AK, Lee YY. Neurophysiological symptoms and aspartame: What is the connection? Nutr Neurosci. 2017 Feb 15:1-11. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2017.1288340
Choudhary AK, Devi RS. Effects of aspartame on hsp70, bcl-2 and bax expression in immune organs of Wistar albino rats. J Biomed Res. 2016 Sep;30(5):427-435
Choudhary AK, Devi RS. Imbalance of the oxidant - antioxidant status by aspartame in the organs of immune system of Wistar albino rats. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol. 2014; 8(8);220-230
Choudhary AK, Rathinasamy SD. Aspartame induces alteration in electrolytes homeostasis of immune organs in wistar albino rats[J]. Biomedicine and Preventive Nutrition, 2014, 4: 181–187
Choudhary AK, Rathinasamy SD. Effect of long intake of aspartame on ionic imbalance in immune organs of immunized wistar albino rats[J]. Biomedicine and Aging Pathology, 2014, 4: 243–249
Choudhary AK, Devi RS. Effect of long intake of aspartame on oxidative stress and cell and humoral immune response in immunized wistar albino rats. Am J PharmTech Res. 2014 (2)
Choudhary AK, Devi RS. Serum biochemical responses under oxidative stress of aspartame in wistar albino rats. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 2014; 4(1):930-937
Choudhary AK, Sundareswaran L, Devi RS. Aspartame induced cardiac oxidative stress in Wistar albino rats. Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme. 2016; 30; 10.1016/j.nupar.2016.01.071
Choudhary AK, Sundareswaran L, Devi RS. Effects of aspartame on the evaluation of electrophysiological responses in Wistar albino rats. Journal of Taibah University for Science. 2015; 10; 10.1016/j.jtusci.2015.07.006
Pereira MA. Sugar-sweetened and artificially-sweetened beverages in relation to obesity risk. Adv Nutr. 2014 Nov 14;5(6):797-808
Rogers PJ, Hogenkamp PS et al. Does low-energy sweetener consumption affect energy intake and body weight? A systematic review, including meta-analyses, of the evidence from human and animal studies. Int J Obes (Lond). 2016 Mar;40(3):381-94
Lohner S, Toews I, Meerpohl JJ. Health outcomes of non-nutritive sweeteners: analysis of the research landscape. Nutr J. 2017 Sep 8;16(1):55
Olivier B, Serge AH et al. Review of the nutritional benefits and risks related to intense sweeteners. Arch Public Health. 2015 Oct 1;73:41
Kuk JL, Brown RE. Aspartame intake is associated with greater glucose intolerance in individuals with obesity. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016 Jul;41(7):795-8
Yang Q. Gain weight by "going diet?" Artificial sweeteners and the neurobiology of sugar cravings: Neuroscience 2010. Yale J Biol Med. 2010 Jun;83(2):101-8
Hill SE, Prokosch ML et al. The effect of non-caloric sweeteners on cognition, choice, and post-consumption satisfaction. Appetite. 2014 Dec;83:82-8
Fowler SPG. Low-calorie sweetener use and energy balance: Results from experimental studies in animals, and large-scale prospective studies in humans. Physiol Behav. 2016 Oct 1;164(Pt B):517-523
http://www.wur.nl/nl/nieuws/Light-maakt-ook-op-de-lange-termijn-niet-sla...
Scientific Committee on Food. Opinion of the Scientific Committee on Food: Update on the Safety of Aspartame. 10 december 2002
Glushakov AV, Dennis DM et al. L-phenylalanine selectively depresses currents at glutamatergic excitatory synapses. J Neurosci Res. 2003 Apr 1;72(1):116-24
Zaeem Z, Zhou L, Dilli E. Headaches: a review of the role of dietary factors. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2016 Nov;16(11):101
Alcohol and cancer. Lancet. 2017; 390(18):2215
Sylvetsky AC et al. Nonnutritive sweeteners in breast milk. J Toxic Environ Health. 2015; A 78:1029–1032
Borthwick AD, Da Costa NC. 2,5-diketopiperazines in food and beverages: Taste and bioactivity. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Mar 4;57(4):718-742
Sylvetsky AC, Conway EM et al. Development of sweet taste perception: Implications for artificial sweetener use. Endocr Dev. 2017;32:87-99. doi: 10.1159/000475733. Epub 2017 Aug 15.
Beauchamp GK. Why do we like sweet taste: A bitter tale? Physiol Behav. 2016 Oct 1;164(Pt B):432-437
Tey SL, Salleh NB et al. Effects of aspartame-, monk fruit-, stevia- and sucrose-sweetened beverages on postprandial glucose, insulin and energy intake. Int J Obes (Lond). 2017 Mar;41(3):450-457
Tey SL, Salleh NB et al. Effects of non-nutritive (artificial vs natural) sweeteners on 24-h glucose profiles. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2017 Sep;71(9):1129-1132
Santos NC, de Araujo LM et al. Metabolic effects of aspartame in adulthood: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2017 Apr 10:1-14
Gombos K, Varjas T, Orsós Z et al. The effect of aspartame administration on oncogene and suppressor gene expressions. In Vivo. 2007 Jan-Feb;21(1):89-92
Paolini M, Vivarelli F et al. Aspartame, a bittersweet pill. Carcinogenesis. 2016 Feb 24. pii: bgw025
McCullough ML, Teras LR et al. Artificially and sugar-sweetened carbonated beverage consumption is not associated with risk of lymphoid neoplasms in older men and women. J Nutr. 2014 Dec;144(12):2041-9
Low YQ, Lacy K, Keast R. The role of sweet taste in satiation and satiety. Nutrients. 2014 Sep 2;6(9):3431-50
Nosti-Palacios R, Gómez-Garduño J et al. Aspartame administration and insulin treatment altered brain levels of CYP2E1 and CYP3A2 in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int J Toxicol. 2014 Jul;33(4):325-331
Cho ES, Coon JD, Stegink LD. Plasma and urine diketopiperazine concentrations in normal adults ingesting large quantities of aspartame. Food Chem Toxicol. 1987 Jul;25(7):499-504