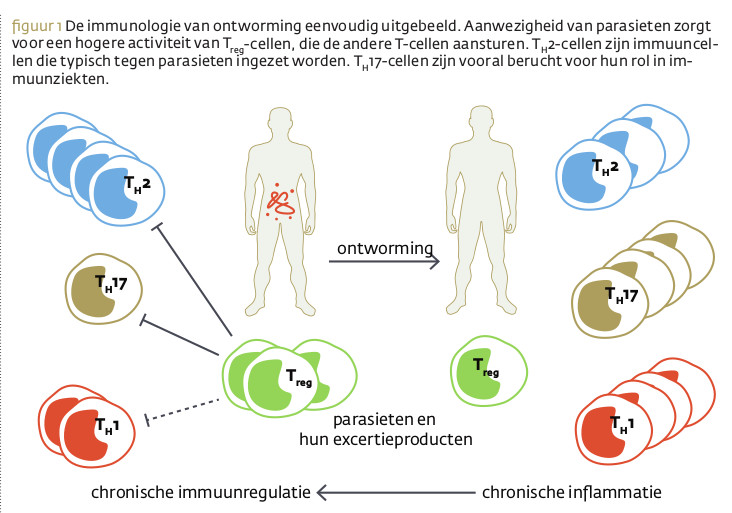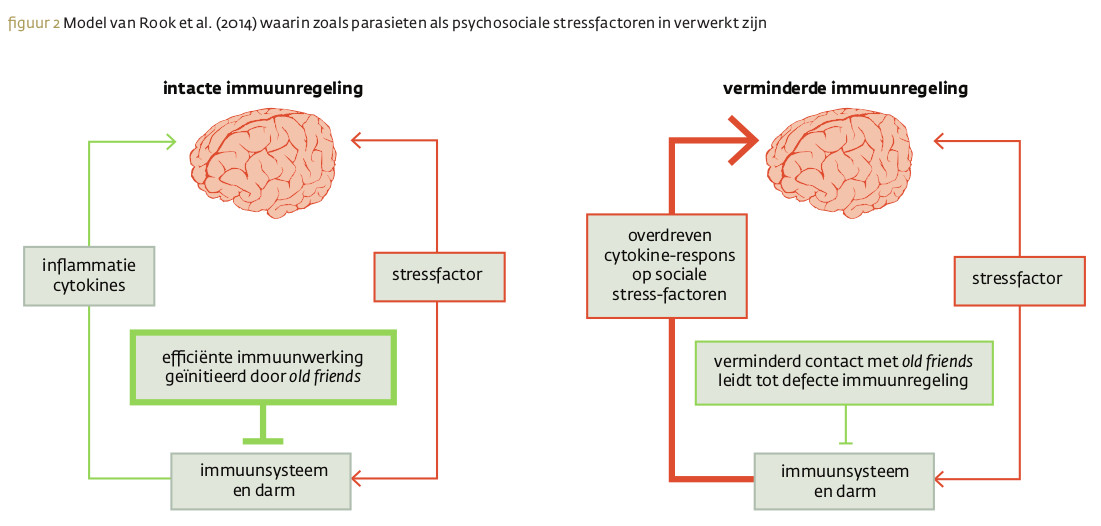
De hygiënehypothese biedt een sterke verklaring voor de
sterke toename van allergie en auto-immuunziekten in de westerse
wereld. Parasieten zijn niet meer weg te denken uit de
hygiënehypothese. Slechts een handvol klinische studies zijn tot
nu toe uitgevoerd op mensen die zich laten infecteren met
parasieten. Gek genoeg zijn er meer reviews over dit onderwerp te
vinden dan klinische studies. Dat is wel een teken dat
onderzoekers wild enthousiast zijn over het therapeutisch
potentieel van parasieten. De resultaten van klinische studies
onderschrijven dit enthousiasme alsnog niet.
Beste bezoeker, u heeft geen toegang.
Enkel (web)abonnees hebben toegang tot tijdschriftartikelen. Het webabonnement is nog in de maak.
U kunt zich wel alvast (gratis) registreren en tal van andere webartikelen raadplegen!
Auteur
Verschenen in
Referenties
Bager P, Arnved J, Rønborg S et al. Trichuris suis ova therapy for allergic rhinitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Jan;125(1):123-30.e1-3
Bager P, Kapel C, Roepstorff A et al. Symptoms after ingestion of pig whipworm Trichuris suis eggs in a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e22346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022346
Blackley CH (1873) Experimental researches on the causes and nature of catarrhus aestivus (Hay-fever and Hay-asthma). Baillière Tindall and Cox, London
Bourke CD, Mutapi F, Nausch N et al. Trichuris suis ova therapy for allergic rhinitis does not affect allergen-specific cytokine responses despite a parasite-specific cytokine response. Clin Exp Allergy. 2012 Nov;42(11):1582-95
Correale J, Farez M, Razzitte G. Helminth infections associated with multiple sclerosis induce regulatory B cells. Ann Neurol. 2008 Aug;64(2):187-99
Correale J, Farez M. Association between parasite infection and immune responses in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 2007; 61:97–1
Correale J, Farez MF. The impact of parasite infections on the course of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 2011 Apr;233(1-2):6-11
Croese J, Giacomin P, Navarro S et al. Experimental hookworm infection and gluten microchallenge promote tolerance in celiac disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Feb;135(2):508-16
Croese J, O'neil J, Masson J et al. A proof of concept study establishing Necator americanus in Crohn's patients and reservoir donors. Gut. 2006 Jan;55(1):136-7
Daley D. The evolution of the hygiene hypothesis: the role of early-life exposures to viruses and microbes and their relationship to asthma and allergic diseases. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014 Oct;14(5):390-6
Daveson AJ, Jones DM, Gaze S et al. Effect of hookworm infection on wheat challenge in celiac disease--a randomised double-blinded placebo controlled trial. PLoS One. 2011 Mar 8;6(3):e17366
Ditgen D, Anandarajah EM, Meissner KA et al. Harnessing the helminth secretome for therapeutic immunomodulators. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:964350
Feary JR, Venn AJ, Mortimer K et al. Experimental hookworm infection: a randomized placebo-controlled trial in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2010 Feb;40(2):299-306
Fleming JO, Isaak A, Lee JE et al. Probiotic helminth administration in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a phase 1 study. Mult Scler. 2011 Jun;17(6):743-54
Giacomin P, Zakrzewski M, Croese J et al. Experimental hookworm infection and escalating gluten challenges are associated with increased microbial richness in celiac subjects. Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 18;5:13797
Greenwood BM. Autoimmune disease and parasitic infections in Nigerians. Lancet. 1968;2:380–2
Harnett MM, Melendez AJ, Harnett W. The therapeutic potential of the filarial nematode-derived immunodulator, ES-62 in inflammatory disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Mar;159(3):256-67
Hunter MM, Wang A, McKay DM. Helminth infection enhances disease in a murine TH2 model of colitis. Gastroenterology. 2007 Apr;132(4):1320-30
Kaiser J. Will an aspirin a day keep cancer away? Science. 2012 Sep 21;337(6101):1471-3
Khan AR, Fallon PG. Helminth therapies: translating the unknown unknowns to known knowns. Int J Parasitol. 2013 Mar;43(3-4):293-9
Lu L, Nanus M, Forman S. Coronado biosciences announces top-line results from its TRUST-I phase 2 clinical trial of TSO for the treatment of Crohn’s disease. http://globenewswire.com/news-release/2013/10/14/580190/10052399/en/Coro...
Maizels RM, McSorley HJ, Smyth DJ. Helminths in the hygiene hypothesis: sooner or later? Clin Exp Immunol. 2014 Jul;177(1):38-46
Malhotra I, Ouma JH, Wamachi A et al. Influence of maternal filariasis on childhood infection and immunity to Wuchereria bancrofti in Kenya. Infect Immun. 2003 Sep;71(9):5231-7
McKay DM. Not all parasites are protective. Parasite Immunol. 2015 Jun;37(6):324-32
McSorley HJ, Gaze S, Daveson J et al. Suppression of inflammatory immune responses in celiac disease by experimental hookworm infection. PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e24092
Oikonomopoulou K, Brinc D, Kyriacou K et al. Infection and cancer: revaluation of the hygiene hypothesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Jun 1;19(11):2834-41
Parker W. The "hygiene hypothesis" for allergic disease is a misnomer. BMJ. 2014 Aug 26;348:g5267
Pritchard DI. Worm therapy: How would you like your medicine? Int J Parasitol Drugs Drug Resist. 2012 Mar 2;2:106-8
Rook GA, Dalgleish A. Infection, immunoregulation, and cancer. Immunol Rev. 2011 Mar;240(1):141-59
Rook GA, Raison CL, Lowry CA. Microbial 'old friends', immunoregulation and socioeconomic status. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014 Jul;177(1):1-12
Rook GA, Raison CL, Lowry CA. Microbiota, immunoregulatory old friends and psychiatric disorders. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;817:319-56
Rook GA. Hygiene and other early childhood influences on the subsequent function of the immune system. Dig Dis. 2011;29(2):144-53
Rook GA. Hygiene hypothesis and autoimmune diseases. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012 Feb;42(1):5-15
Sandborn WJ, Elliott DE, Weinstock J et al. Randomised clinical trial: the safety and tolerability of Trichuris suis ova in patients with Crohn's disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Aug;38(3):255-63
Scanlon ST, McKenzie AN. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells: new players in asthma and allergy. Curr Opin Immunol. 2012 Dec;24(6):707-12
Schaub B, Lauener R, von Mutius E. The many faces of the hygiene hypothesis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006 May;117(5):969-77
Siniscalco D, Antonucci N. Possible use of Trichuris suis ova in autism spectrum disorders therapy. Med Hypotheses. 2013 Jul;81(1):1-4
Strachan DP, Aït-Khaled N, Foliaki S et al. Siblings, asthma, rhinoconjunctivitis and eczema: a worldwide perspective from the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015 Jan;45(1):126-36
Strachan DP. Hay fever, hygiene, and household size. BMJ. 1989 Nov 18;299(6710):1259-60
Summers RW, Elliott DE, Qadir K et al. Trichuris suis seems to be safe and possibly effective in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2003 Sep;98(9):2034-41
Summers RW, Elliott DE, Urban JF Jr et al. Trichuris suis therapy in Crohn's disease. Gut. 2005 Jan;54(1):87-90
Ursell LK, Van Treuren W, Metcalf JL et al. Replenishing our defensive microbes. Bioessays. 2013 Sep;35(9):810-7
van den Biggelaar AH, Rodrigues LC, van Ree R et al. Long-term treatment of intestinal helminths increases mite skin-test reactivity in Gabonese schoolchildren. J Infect Dis. 2004 Mar 1;189(5):892-900
Wammes LJ, Mpairwe H, Elliott AM et al. Helminth therapy or elimination: epidemiological, immunological, and clinical considerations. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014 Nov;14(11):1150-62
Williamson LL, McKenney EA, Holzknecht ZE et al. Got worms? Perinatal exposure to helminths prevents persistent immune sensitization and cognitive dysfunction induced by early-life infection. Brain Behav Immun. 2015 Jul 7. pii: S0889-1591(15)00240-8