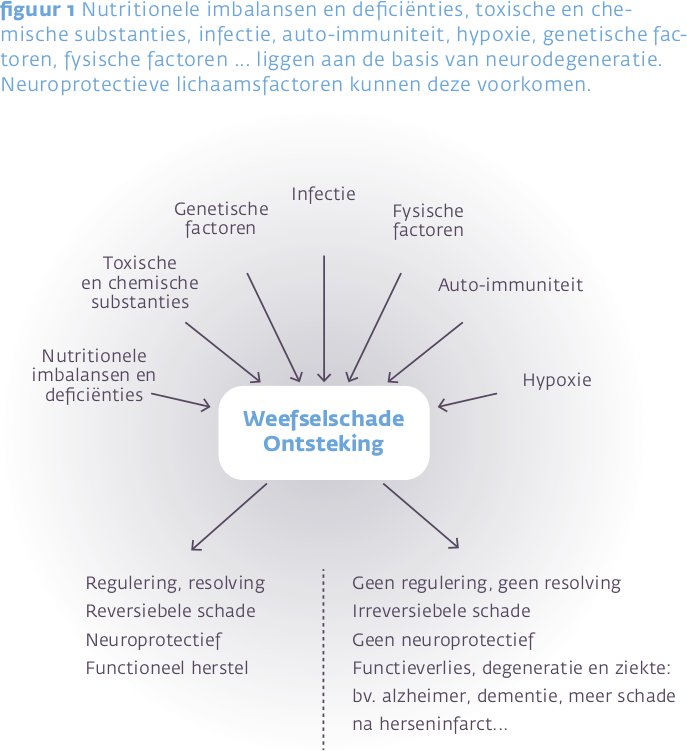
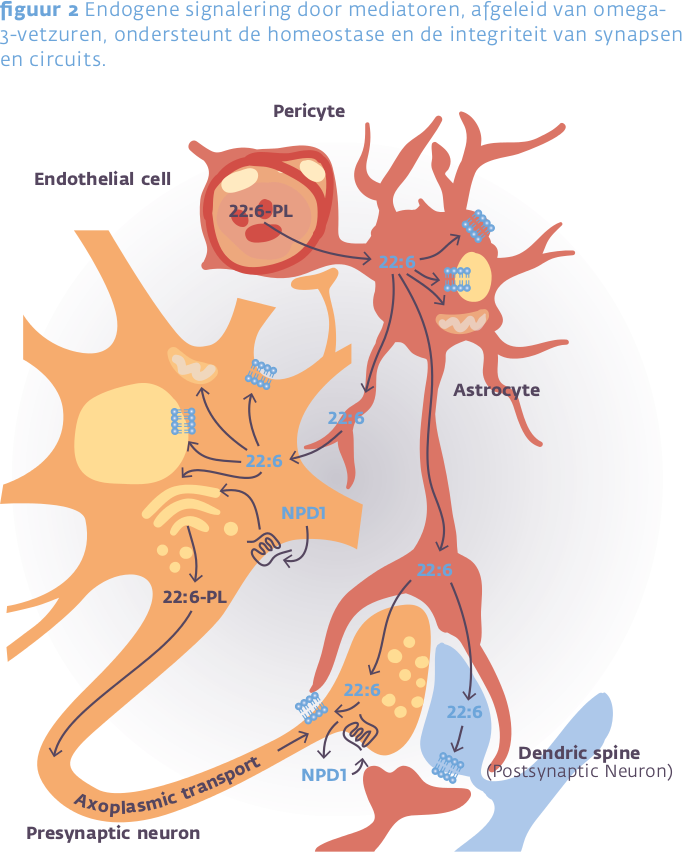
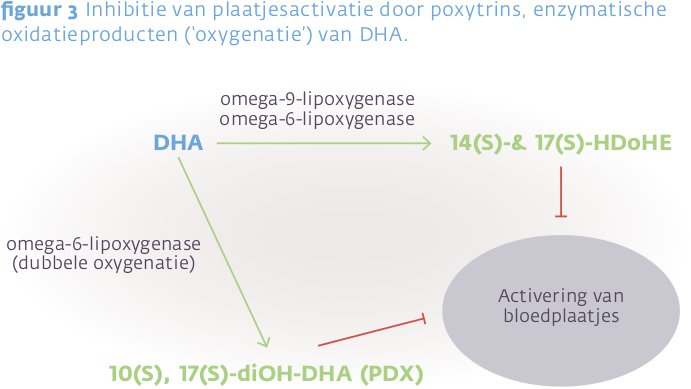
Epidemiologische studies tonen een duidelijke correlatie tussen een hoge visconsumptie en een lager risico op cognitieve achteruitgang. Ook in dierproeven is aangetoond dat DHA cognitieve achteruitgang gedeeltelijk kan tegengaan, en het risico op geheugenstoornissen en alzheimer kan verlagen.
Beste bezoeker, u heeft geen toegang.
Enkel (web)abonnees hebben toegang tot tijdschriftartikelen. Het webabonnement is nog in de maak.
U kunt zich wel alvast (gratis) registreren en tal van andere webartikelen raadplegen!
Auteur
Trefwoorden:
Verschenen in
Referenties
Solfrizzi V, Panza F, Frisardi V, Seripa D, Logroscino G, Imbimbo BP, Pilotto A. Diet and Alzheimer's disease risk factors or prevention: the current evidence. Expert Rev Neurother. 2011 May;11(5):677-708.
Huang TL. Omega-3 fatty acids, cognitive decline, and Alzheimer's disease: a critical review and evaluation of the literature. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;21(3):673-90.
Solfrizzi V, Frisardi V, Capurso C, D'Introno A, Colacicco AM, Vendemiale G, Capurso A, Panza F. Dietary fatty acids in dementia and predementia syndromes: epidemiological evidence and possible underlying mechanisms. SourceAgeing Res Rev. 2010 Apr;9(2):184-99.
Fotuhi M, Mohassel P, Yaffe K. Fish consumption, long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and risk of cognitive decline or Alzheimer disease: a complex association. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2009 Mar;5(3):140-52.
Solfrizzi V, Frisardi V, Capurso C, D'Introno A, Colacicco AM, Vendemiale G, Capurso A, Panza F. Dietary fatty acids and predementia syndromes. ScientificWorldJournal. 2009 Aug 11;9:792-810.
Schwarz M, Purimboom L. Resoleomics. Cursus PNI, 2e jaar. www.Vannature.nl
Chiang N, Arita M, Serhan CN. Anti-inflammatory circuitry: Lipoxin, aspirin-triggered lipoxins and their receptor ALX$. Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids 73 (2005) 163–177
Reichardt LF. Neurotrophin--regulated signalling pathways. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2006 361, 1545-1564
Niemoller TD, Stark DT, Bazan NG. Omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid is the precursor of neuroprotectin D1 in the nervous system. World Rev Nutr Diet. 2009;99:46-54.
Stark DT, Bazan NG. Neuroprotectin D1 induces neuronal survival and downregulation of amyloidogenic processing in Alzheimer's disease cellular models. Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Apr;43(2):131-8.
Zhao Y, Calon F, Julien C, Winkler JW, Petasis NA, Lukiw WJ, Bazan NG. Docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1 induces neuronal survival via secretase- and PPARγ-mediated mechanisms in Alzheimer's disease models. PLoS One. 2011 Jan 5;6(1):e15816.
Bazan NG. Cellular and molecular events mediated by docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1 signaling in photoreceptor cell survival and brain protection. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2009 Aug-Sep;81(2-3):205-11.
Bazan NG, Marcheselli VL, Cole-Edwards K. Brain response to injury and neurodegeneration: endogenous neuroprotective signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Aug;1053:137-47.
Picq M, Chen P, Perez M, Michaud M, Véricel E, Guichardant M, Lagarde M. DHA metabolism: targeting the brain and lipoxygenation. Mol Neurobiol. 2010 Aug;42(1):48-51.
Chen P, Véricel E, Lagarde M, Guichardant M. Poxytrins, a class of oxygenated products from polyunsaturated fatty acids, potently inhibit blood platelet aggregation. FASEB J. 2011 Jan;25(1):382-8.
Serhan CN, Gotlinger K, Hong S, Lu Y, Siegelman J, Baer T, Yang R, Colgan SP, Petasis NA. Anti-inflammatory actions of neuroprotectin D1/protectin D1 and its natural stereoisomers: assignments of dihydroxy-containing docosatrienes. J Immunol. 2006 Feb 1;176(3):1848-59.
Lukiw WJ, Bazan NG. Inflammatory, apoptotic, and survival gene signaling in Alzheimer's disease. A review on the bioactivity of neuroprotectin D1 and apoptosis. Mol Neurobiol. 2010 Aug;42(1):10-6.
Bazan NG. Neuroprotectin D1-mediated anti-inflammatory and survival signaling in stroke, retinal degenerations, and Alzheimer's disease. J Lipid Res. 2009 Apr;50 Suppl:S400-5.
Lukiw WJ, Cui JG, Marcheselli VL, Bodker M, Botkjaer A, Gotlinger K, Serhan CN, Bazan NG. A role for docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1 in neural cell survival and Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest. 2005 Oct;115(10):2774-83.
Bazan NG, Colangelo V, Lukiw WJ. Prostaglandins and other lipid mediators in Alzheimer's disease. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002 Aug;68-69:197-210.
Bazan NG, Molina MF, Gordon WC. Docosahexaenoic acid signalolipidomics in nutrition: significance in aging, neuroinflammation, macular degeneration, Alzheimer's, and other neurodegenerative diseases. Annu Rev Nutr. 2011 Aug 21;31:321-51.
Niemoller TD, Bazan NG. Docosahexaenoic acid neurolipidomics. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2010 Apr;91(3-4):85-9.
Palacios-Pelaez R, Lukiw WJ, Bazan NG. Omega-3 essential fatty acids modulate initiation and progression of neurodegenerative disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2010 Jun;41(2-3):367-74.
Belayev L, Khoutorova L, Atkins KD, Bazan NG. Robust docosahexaenoic acid-mediated neuroprotection in a rat model of transient, focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 2009 Sep;40(9):3121-6.
Bazan NG, Musto AE, Knott EJ. Endogenous signaling by omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid-derived mediators sustains homeostatic synaptic and circuitry integrity. Mol Neurobiol. 2011 Oct;44(2):216-22.
Stark DT, Bazan NG. Synaptic and extrasynaptic NMDA receptors differentially modulate neuronal cyclooxygenase-2 function, lipid peroxidation, and neuroprotection. J Neurosci. 2011 Sep 28;31(39):13710-21.
Moeilijke uitleg NMDAreceptoren lees in andere studies bazan (begin) EN Word NMDAreceptoren
Chen C, Bazan NG. Lipid signaling: sleep, synaptic plasticity, and neuroprotection. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2005 Sep;77(1-4):65-76.
Bazan NG. The onset of brain injury and neurodegeneration triggers the synthesis of docosanoid neuroprotective signaling. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006 Jul-Aug;26(4-6):901-13.
Solfrizzi V, Frisardi V, Seripa D, Logroscino G, Imbimbo BP, D'Onofrio G, Addante F, Sancarlo D, Cascavilla L, Pilotto A, Panza F. Mediterranean diet in predementia and dementia syndromes. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2011 Aug;8(5):520-42.
Bazan NG, Molina MF, Gordon WC. Docosahexaenoic acid signalolipidomics in nutrition: significance in aging, neuroinflammation, macular degeneration, Alzheimer's, and other neurodegenerative diseases. Annu Rev Nutr. 2011 Aug 21;31:321-51.