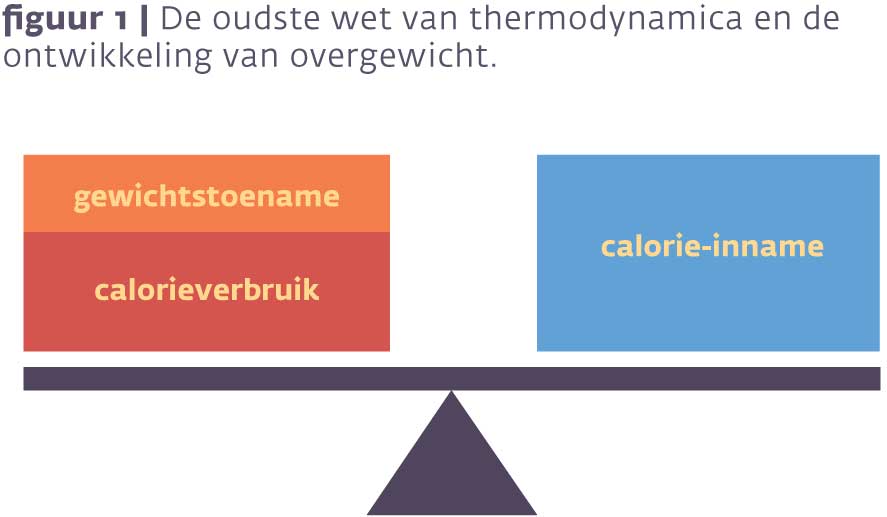
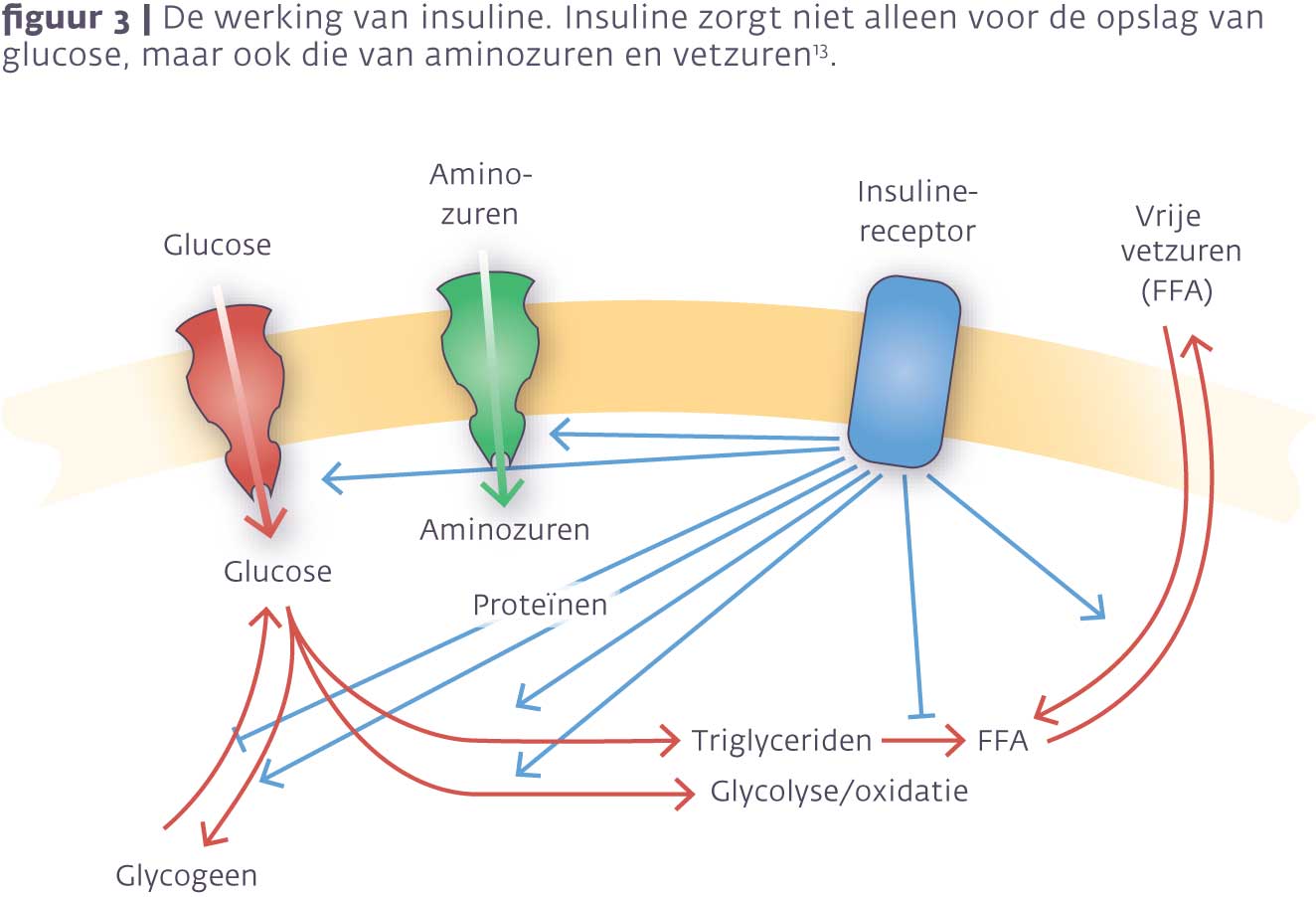
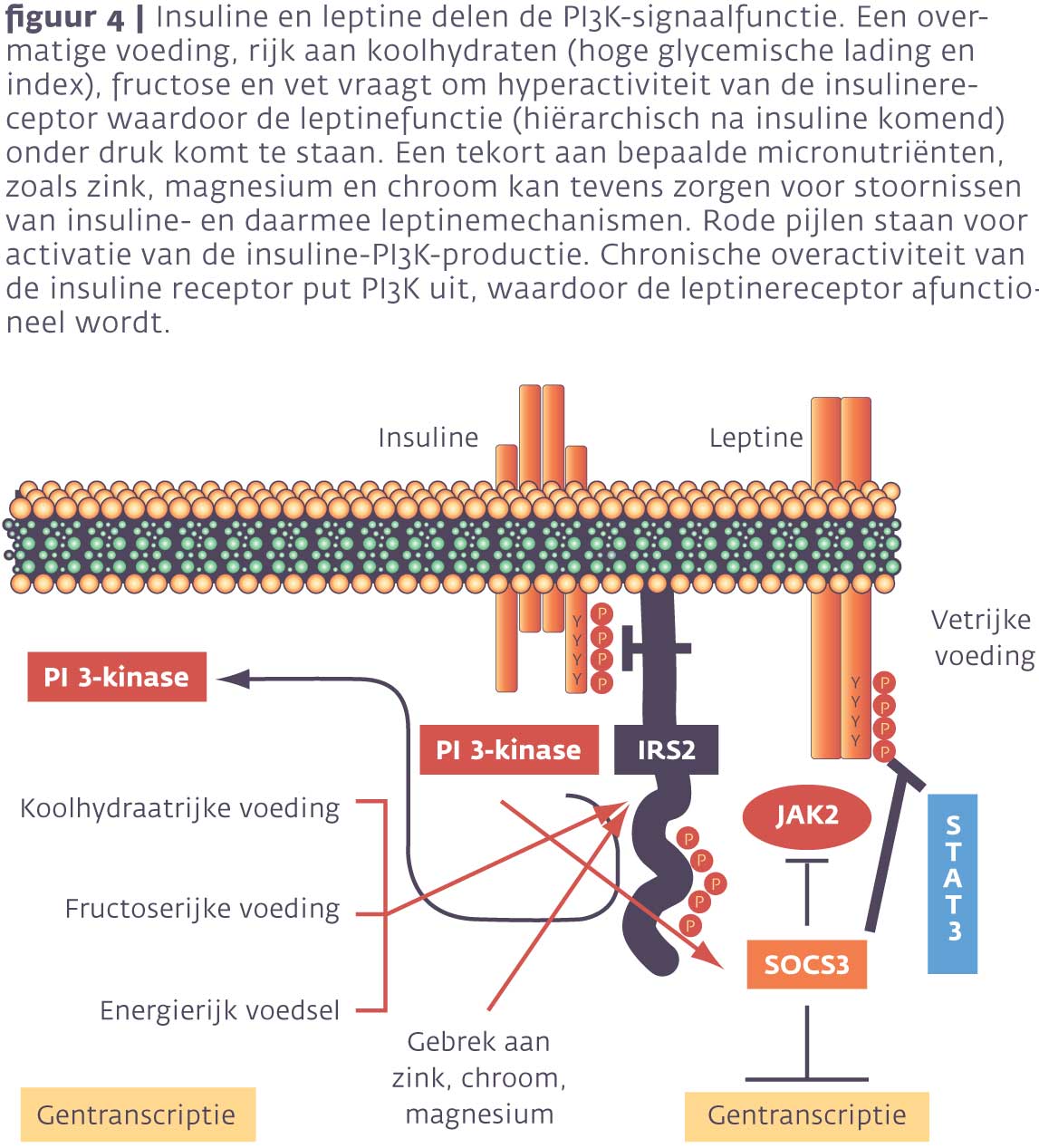
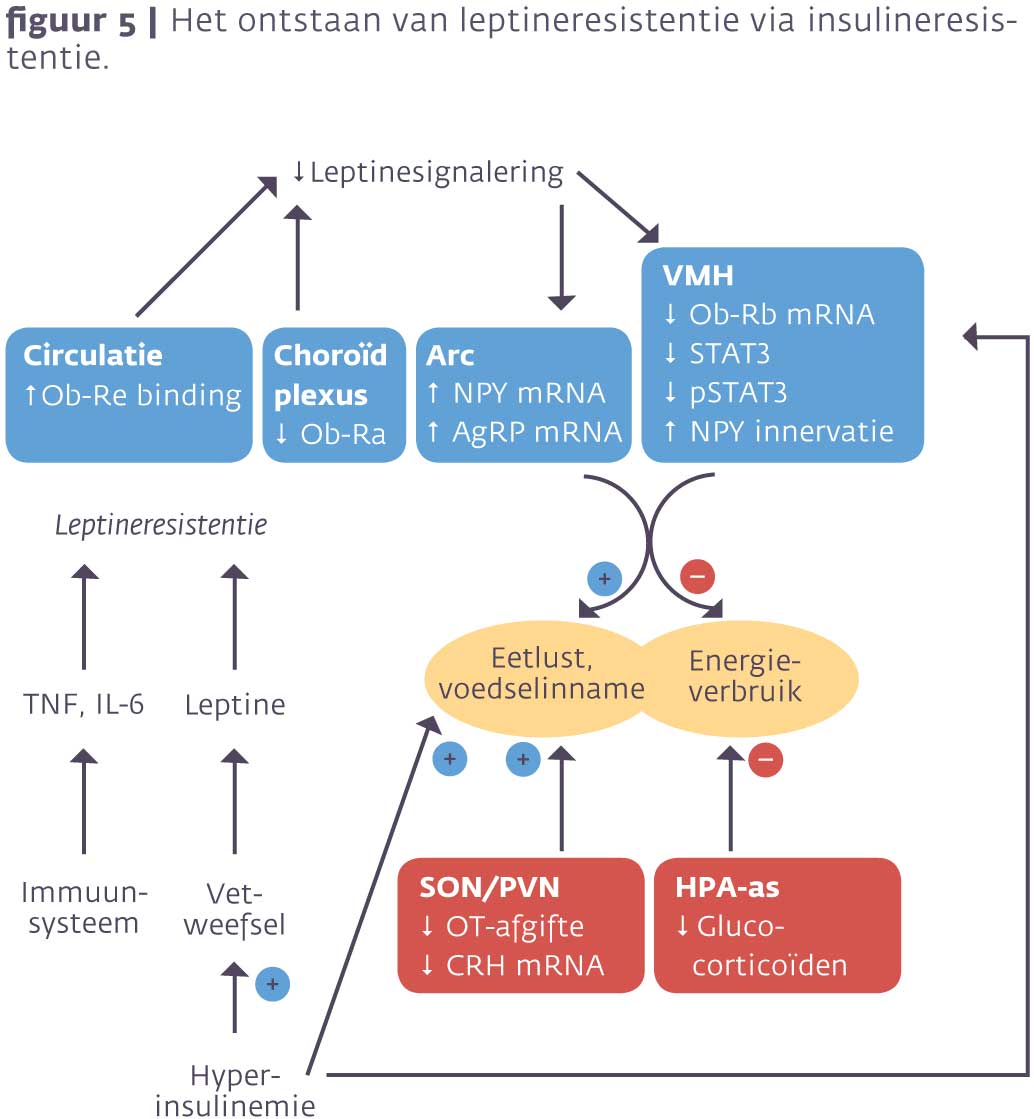
Insulineresistentie en overgewicht zijn twee factoren die de laatste dertig jaar sterk zijn toegenomen. Oorzaken zijn gelegen in vooral verandering van gedrag, voeding en beweging. Simpel gezegd ontstaat overgewicht door de inname van een grotere hoeveelheid caloriën dan verbruikt wordt, oftewel de oudste wet van thermodynamica (zie afbeelding 1) 1,2.
Beste bezoeker, u heeft geen toegang.
Enkel (web)abonnees hebben toegang tot tijdschriftartikelen. Het webabonnement is nog in de maak.
U kunt zich wel alvast (gratis) registreren en tal van andere webartikelen raadplegen!
Auteur
Verschenen in
Referenties
1. Ludwig DS. Diet and development of the insulin resistance syndrome. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2003;12 Suppl:S4
2. Isganaitis E, Lustig RH. Fast food, central nervous system insulin resistance, and obesity. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005;25(12): 2451-62
3. Teff KL, Grudziak J, et al. Endocrine and metabolic effects of consuming fructose- and glucose-sweetened beverages with meals in obese men and women: influence of insulin resistance on plasma triglyceride responses. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009;94(5): 1562-9
4. Dufour JF Oneta CM. Alcoholic and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis]. Ther Umsch 2004;61(8): 505-12
5. Kral TV, Rolls BJ. Energy density and portion size: their independent and combined effects on energy intake. Physiol Behav 2004;82(1): 131-8
6. Schaefer EJ, Gleason JA, et al. Dietary fructose and glucose differentially affect lipid and glucose homeostasis. J Nutr 2009;139(6): 1257S-1262S
7. Dorfman SE, Laurent D, et al. Metabolic implications of dietary trans-fatty acids. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2009;17(6): 1200-7
8. Bradley R, Oberg EB, et al. Algorithm for complementary and alternative medicine practice and research in type 2 diabetes. J Altern Complement Med 2007;13(1): 159-75
9. Kien CL. Dietary interventions for metabolic syndrome: role of modifying dietary fats. Curr Diab Rep 2009;9(1): 43-50
10. Han JC, Rutledge MS, et al. Insulin resistance, hyperinsulinemia, and energy intake in overweight children. J Pediatr 2008;152(5): 612-7, 617 e1
11. Pereira MA, Kartashov AI, et al. Fast-food habits, weight gain, and insulin resistance (the CARDIA study): 15-year prospective analysis. Lancet 2005;365(9453): 36-42
12. Lustig RH. Childhood obesity: behavioral aberration or biochemical drive? Reinterpre-ting the First Law of Thermodynamics. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2006;2(8): 447-58
13. Saltiel AR, Kahn CR. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 2001;414(6865): 799-806
14. Shalev U, Yap J, Shaham Y. Leptin attenuates food deprivation-induced relapse to heroin seeking. J Neurosci. 2001;21:RC129:1–5
15. Kawai K, Sugimoto K, Nakashima K, et al. Leptin as a modulator of sweet taste sensitivities in mice. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA.2000;97:11044–11049
16. Oppert JM, Nadeau A, Tremblay A, et al. Plasma glucose, insulin, and glucagon before and after long-term overfeeding in identical twins. Metabolism 1995;44:96-105
17. Goodpaster BH, Kelley DE, Wing RR, et al. Effects of weight loss on regional fat distribution and insulin sensitivity in obesity. Diabetes 1999;48:839-847
18. Muoio DM, Koves TR. Lipid-induced metabolic dysfunction in skeletal muscle. Novartis Found Symp 2007;286: 24-38; discussion 38-46, 162-3, 196-203
19. Corpeleijn E, Saris WH, et al. Metabolic flexibility in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: effects of lifestyle. Obes Rev 2009;10(2): 178-93
20. Ebbesson SO, Tejero ME, et al. Fatty acid consumption and metabolic syndrome components: the GOCADAN study. J Cardiometab Syndr 2007;2(4): 244-9
21. Ledikwe JH, Ello-Martin JA, et al. Portion sizes and the obesity epidemic. J Nutr 2005;135(4): 905-9
22. Mozaffarian D, Willett WC. Trans fatty acids and cardiovascular risk: a unique cardiometabolic imprint? Curr Atheroscler Rep 2007;9(6): 486-93
23. Muniyappa R, Lantorno M, et al. An integrated view of insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2008;37(3): 685-711, ix-x
24. Natali A, Toschi E, et al. Clustering of insulin resistance with vascular dysfunction and low-grade inflammation in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2006;55(4): 1133-40
25. Ye J. Role of insulin in the pathogenesis of free fatty acid-induced insulin resistance in skeletal mu Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2007;7(1): 65-74
26. Lionetti L, Mollica MP, et al. From chronic overnutrition to insulin resistance: the role of fat-storing capacity and inflammation. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 19(2): 146-52.
27. Barnes KM, Miner JL. Role of resistin in insulin sensitivity in rodents and humans. Curr Protein Pept Sci 2009;10(1): 96-107
28. Qatanani M, Szwergold NR, et al. Macrophage-derived human resistin exacerbates adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in mice. J Clin Invest. 2009
29. Banks WA. The source of cerebral insulin. Eur J Pharmacol 2004;490(1-3): 5-12
30. Brunton PJ, Russell JA. The expectant brain: adapting for motherhood. Nat Rev Neurosci 2008;9(1):11-25
31. Erlanson-Albertsson C. How palatable food disrupts appetite regulation. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2005;97(2): 61-73
32. Luchsinger JA, Gustafson DR. Adiposity, type 2 diabetes, and Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2009;16(4):693-704
33. Craft S. The role of metabolic disorders in Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia: two roads converged. Arch Neurol 2009;66(3):300-5
34. Rolls BJ, Castellanos VH, et al. Volume of food consumed affects satiety in men. Am J Clin Nutr 1998;67(6):1170-7
35. Rolls BJ, Drewnowski JA, et al. Changing the energy density of the diet as a strategy for weight management. J Am Diet Assoc 2005;105(5 Suppl 1): S98-103
36. McNaughton SA, Mishra GD, et al. Dietary patterns, insulin resistance, and incidence of type 2 diabetes in the Whitehall II Study. Diabetes Care 2008;31(7):1343-8
37. Rallidis LS, Lekakis J, et al. Close adherence to a Mediterranean diet improves endothelial function in subjects with abdominal obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 2009;90(2): 263-8
38. Liese AD, Weis KE, et al. Food intake patterns associated with incident type 2 diabetes: the Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study. Diabetes Care 2009;32(2):263-8
39. Mao CP, Xie ML, et al. Effects of konjac extract on insulin sensitivity in high fat diet rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2002;23(9): 855-9
40. Vuksan V, Sievenpiper Jl, et al. Beneficial effects of viscous dietary fiber from Konjacmannan in subjects with the insulin resistance syndrome: results of a controlled metabolic trial. Diabetes Care 2000;23(1): 9-14
41. Vuksan V, Sievenpiper JL, et al. Konjac-Mannan and American ginsing: emerging alternative therapies for type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Nutr 2001; 20(5 Suppl): 370S-380S; discussion 381S-383S
42. Cani PD, Delzenne NM. The role of the gut microbiota in energy metabolism and metabolic disease. Curr Pharm Des 2009;15(13): 1546-58
43. Reimer RA, Russell JC. Glucose tolerance, lipids, and GLP-1 secretion in JCR:LA-cp rats fed a high protein fiber diet. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2008;16(1): 40-6
44. Roberfroid MB. Prebiotics and probiotics: are they functional foods? Am J Clin Nutr 2000;71(6 Suppl): 1682S-7S; discussion 1688S-90S
45. Tsitouras PD, Gucciardo F, et al. High omega-3 fat intake improves insulin sensitivity and reduces CRP and IL6, but does not affect other endocrine axes in healthy older adults. Horm Metab Res 2008;40(3):199-205
46. Lankinen M, Schwab U, et al. Fatty fish intake decreases lipids related to inflammation and insulin signaling--a lipidomics approach. PLoS One 2009;4(4):e5258
47. Fedor D, Kelley DS. Prevention of insulin resistance by n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2009;12(2): 138-46
48. Assy N, Nasser G, et al. Soft drink consumption linked with fatty liver in the absence of traditional risk factors. Can J Gastroenterol 2008;22(10): 811-6
49. Dorfman SE, Laurent D, et al. Metabolic implications of dietary trans-fatty acids. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2009;17(6):1200-7
50. Micha R, Mozaffarian D. Trans fatty acids: effects on metabolic syndrome, heart disease and diabetes. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2009;5(6):335-44
51. Balducci S, Zanuso S, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of exercise training in subjects with type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome is dependent on exercise modalities and independent of weight loss. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2009
52. Bajpeyi S, Tanner CJ, et al. Effect of exercise intensity and volume on persistence of insulin sensitivity during training cessation. J Appl Physiol 2009;106(4):1079-85
53. Effect of metformine on the clinical course of gout and insulin resistance. Klin Med (Mosk) 2009;87(7):41-6
54. Inagaki K, Suzuki A, et al. Metformine hydrochloride reduces both acanthosis nigricans and insulin resistance in Japanese young female. Nippon Naika Gakkai Zasshi 2006;95(12):2550-2
55. Bradley R, Oberg EB, et al. Algorithm for complementary and alternative medicine practice and research in type 2 diabetes. J Altern Complement Med 2007;13(1):159-75.