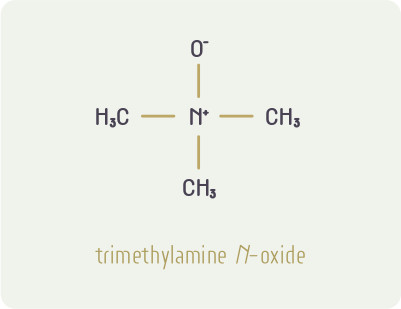
Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) heeft stof doen opwaaien. Het is een metaboliet van choline en carnitine, die weinig goeds lijkt te voorspellen. De afgelopen tien jaar verschenen vooral papers waar aan TMAO een schadelijke invloed toegeschreven werd. De laatste jaren is er wat tegenwind gekomen. Vooral de tegenstrijdigheden vallen nu op, waardoor over de rol van deze marker weinig definitiefs valt te vertellen.
Beste bezoeker, u heeft geen toegang.
Enkel (web)abonnees hebben toegang tot tijdschriftartikelen. Het webabonnement is nog in de maak.
U kunt zich wel alvast (gratis) registreren en tal van andere webartikelen raadplegen!
Auteur
Verschenen in
Referenties
Li D, Lu Y, Yuan S, et al. Gut microbiota-derived metabolite Trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) and multiple health outcomes: an umbrella review and updated meta-analysis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022 Mar 28:nqac074.
Xie G, Yan A, Lin P, et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide-a marker for atherosclerotic vascular disease. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Sep 24;22(3):787-797.
Gatarek P, Kaluzna-Czaplinska J. Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) in human health. EXCLI J. 2021 Feb 11;20:301-319.
Velasquez MT, Ramezani A, Manal A, et al. Trimethylamine N-Oxide: The Good, the Bad and the Unknown. Toxins (Basel). 2016;8(11).
Papandreou C, Moré M, Bellamine A. Trimethylamine N-Oxide in Relation to Cardiometabolic Health-Cause or Effect? Nutrients. 2020 May 7;12(5):1330.
DiNicolantonio JJ, Lavie CJ, Fares H, et al. L-carnitine in the secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Mayo Clin Proc. 2013 Jun;88(6):544-51.
Asbaghi O, Kashkooli S, Amini MR, et al. The effects of L-carnitine supplementation on lipid concentrations inpatients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Cardiovasc Thorac Res. 2020;12(4):246-255.
Fathizadeh H, Milajerdi A, Reiner Ž, et al. The effects of L-carnitine supplementation on indicators of inflammation and oxidative stress: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020 Sep 15;19(2):1879-1894.
Xu Y, Jiang W, Chen G, et al. L-carnitine treatment of insulin resistance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2017 Mar-Apr;26(2):333-338.
Miller CA, Corbin KD, da Costa KA, et al. Effect of egg ingestion on trimethylamine-N-oxide production in humans: a randomized, controlled, dose-response study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;100(3):778-86.
DiMarco DM, Missimer A, Murillo AG, et al. Intake of up to 3 Eggs/Day Increases HDL Cholesterol and Plasma Choline While Plasma Trimethylamine-N-oxide is Unchanged in a Healthy Population. Lipids. 2017;52(3):255-263.
Zhu C, Sawrey-Kubicek L, Bardagjy AS, et al. Whole egg consumption increases plasma choline and betaine without affecting TMAO levels or gut microbiome in overweight postmenopausal women. Nutr Res. 2020;78:36-41.
Lemos BS, Medina-Vera I, Malysheva OV, et al. Effects of Egg Consumption and Choline Supplementation on Plasma Choline and Trimethylamine-N-Oxide in a Young Population. J Am Coll Nutr. 2018 Nov-Dec 37(8):716-723.
Thomas MS, DiBella M, Blesso CN, et al. Comparison between Egg Intake versus Choline Supplementation on Gut Microbiota and Plasma Carotenoids in Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients. 2022;14(6).
Böckmann KA, Franz AR, Minarski M, et al. Differential metabolism of choline supplements in adult volunteers. Eur J Nutr. 2022;61(1):219-230.
Cho CE, Aardema NDJ, Bunnell ML, et al. Effect of Choline Forms and Gut Microbiota Composition on Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Response in Healthy Men. Nutrients. 2020;12(8).
Smith E, Ottosson F, Hellstrand S, et al. Ergothioneine is associated with reduced mortality and decreased risk of cardiovascular disease. Heart. 2020 May;106(9):691-697.
Naghipour S, Cox AJ, Peart JN, et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide: heart of the microbiota-CVD nexus? Nutr Res Rev. 2021 Jun;34(1):125-146.
Li D, Ke Y, Zhan R, et al. Trimethylamine-N-oxide promotes brain aging and cognitive impairment in mice. Aging Cell. 2018 Aug;17(4):e12768.
Kühn T, Rohrmann S, Sookthai D, et al. Intra-individual variation of plasma trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), betaine and choline over 1 year. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017;55(2):261-268.
Gawrys-Kopczynska M, Konop M, Maksymiuk K, et al. TMAO, a seafood-derived molecule, produces diuresis and reduces mortality in heart failure rats. Elife. 2020;9.
Li T, Chen Y, Gua C, et al. Elevated Circulating Trimethylamine N-Oxide Levels Contribute to Endothelial Dysfunction in Aged Rats through Vascular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Front Physiol. 2017;8:350.
Chen K, Zheng X, Feng M, et al. Gut Microbiota-Dependent Metabolite Trimethylamine N-Oxide Contributes to Cardiac Dysfunction in Western Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Front Physiol. 2017;8:139.
Zhu W, Wang Z, Tang WHW, et al. Gut Microbe-Generated Trimethylamine N-Oxide From Dietary Choline Is Prothrombotic in Subjects. Circulation. 2017;135(17):1671-1673.
Trøseid M, Hov JR, Nestvold TK, et al. Major Increase in Microbiota-Dependent Proatherogenic Metabolite TMAO One Year After Bariatric Surgery. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2016;14(4):197-201.
Jomard A, Liberale L, Doytcheva P, et al. Effects of acute administration of trimethylamine N-oxide on endothelial function: a translational study. Sci Rep. 2022 May 23;12(1):8664.
Wang Z, Klipfell E, Bennett BJ, et al. Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature. 2011;472(7341):57-63.
Crimarco A, Springfield S, Petlura C, et al. A randomized crossover trial on the effect of plant-based compared with animal-based meat on trimethylamine-N-oxide and cardiovascular disease risk factors in generally healthy adults: Study With Appetizing Plantfood-Meat Eating Alternative Trial (SWAP-MEAT). Am J Clin Nutr. 2020;112(5):1188-1199.
Koeth RA, Lam-Galvez BR, Kirsop J, et al. l-Carnitine in omnivorous diets induces an atherogenic gut microbial pathway in humans. J Clin Invest. 2019;129(1):373-387.
Dahl WJ, Hung WL, Ford AL, et al. In older women, a high-protein diet including animal-sourced foods did not impact serum levels and urinary excretion of trimethylamine-N-oxide. Nutr Res. 2020 Jun;78:72-81.
Koeth RA, Wang Z, Levison BS, et al. Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat Med. 2013;19(5):576-85.
Argyridou S, Davies MJ, Biddle GJH, et al. Evaluation of an 8-Week Vegan Diet on Plasma Trimethylamine-N-Oxide and Postchallenge Glucose in Adults with Dysglycemia or Obesity. J Nutr. 2021;151(7):1844-1853.
Lombardo M, Aulisa G, Marcon D, et al. The Influence of Animal- or Plant-Based Diets on Blood and Urine Trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO) Levels in Humans. Curr Nutr Rep. 2022;11(1):56-68.
Costabile G, Vetrani C, Bozzetto L, et al. Plasma TMAO increase after healthy diets: results from 2 randomized controlled trials with dietary fish, polyphenols, and whole-grain cereals. Am J Clin Nutr. 2021;114(4):1342-1350.
Griffin LE, Djuric Z, Angiletta CJ, et al. A Mediterranean diet does not alter plasma trimethylamine N-oxide concentrations in healthy adults at risk for colon cancer. Food Funct. 2019 Apr 1;10(4):2138-2147.
Mollar A, Marrachelli VG, Núñez E, et al. Bacterial metabolites trimethylamine N-oxide and butyrate as surrogates of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with a recent decompensated heart failure. Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 17;11(1):6110.
Krueger ES, Lloyd TS, Tessem JS. The Accumulation and Molecular Effects of Trimethylamine N-Oxide on Metabolic Tissues: It’s Not All Bad. Nutrients. 2021 Aug 21;13(8):2873.
Arias N, Arboleya S, Allison J, et al. The Relationship between Choline Bioavailability from Diet, Intestinal Microbiota Composition, and Its Modulation of Human Diseases. Nutrients. 2020;12(8).
Benítez-Páez A, Kjølbæk L, Gómez Del Pulgar EM, et al. A Multi-omics Approach to Unraveling the Microbiome-Mediated Effects of Arabinoxylan Oligosaccharides in Overweight Humans. mSystems. 2019 May 28;4(4):e00209-19.
Zhang C, Yin A, Li H, et al. Dietary Modulation of Gut Microbiota Contributes to Alleviation of Both Genetic and Simple Obesity in Children. EBioMedicine. 2015 Jul 10;2(8):968-84.
Annunziata G, Maisto M, Schisano C, et al. Effects of Grape Pomace Polyphenolic Extract (Taurisolo®) in Reducing TMAO Serum Levels in Humans: Preliminary Results from a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Cross-Over Study. Nutrients. 2019 Jan 10;11(1):139.
Franck M, de Toro-Martín J, Garneau V, et al. Effects of Daily Raspberry Consumption on Immune-Metabolic Health in Subjects at Risk of Metabolic Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients. 2020 Dec 17;12(12):3858.
Cantero MA, Guedes MRA, Fernandes R, et al. Trimethylamine N-oxide reduction is related to probiotic strain specificity: A systematic review. Nutr Res. 2022 Apr 10;104:29-35.
Wu WK, Panyod S, Liu PY, et al. Characterization of TMAO productivity from carnitine challenge facilitates personalized nutrition and microbiome signatures discovery. Microbiome. 2020;8(1):162.
Zeng Y, Guo M, Fang X, et al. Gut Microbiota-Derived Trimethylamine N-Oxide and Kidney Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Adv Nutr. 2021;12(4):1286-1304.
Jia J, Dou P, Gao M, et al. Assessment of Causal Direction Between Gut Microbiota-Dependent Metabolites and Cardiometabolic Health: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Diabetes. 2019;68(9):1747-1755.
Jomard A, Liberale L, Doytcheva P, et al. Effects of acute administration of trimethylamine N-oxide on endothelial function: a translational study. Sci Rep. 2022;12:8664.
Poesen R, Evenepoel P, de Loor H, et al. The influence of prebiotic arabinoxylan oligosaccharides on microbiota derived uremic retention solutes in patients with chronic kidney disease: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0153893.