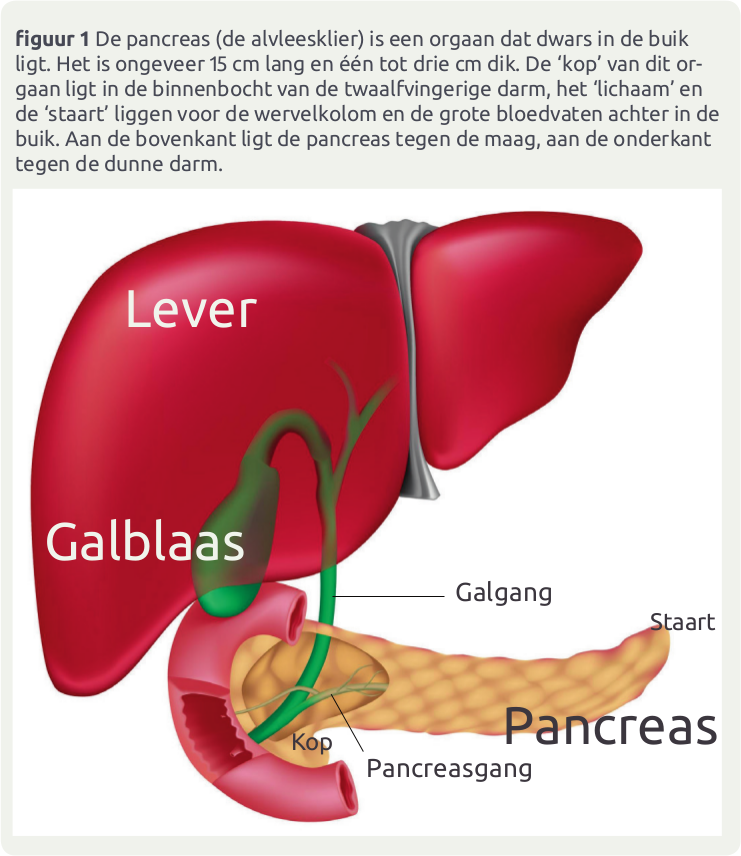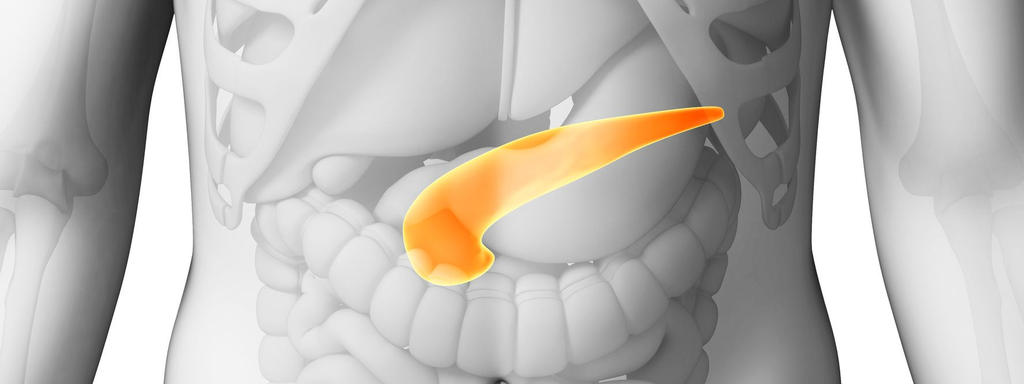
De pancreas of alvleesklier is een wat ‘geheimzinnig’ klein orgaan dat verdoken ligt achterin de buikholte. We weten dat hij insuline aanmaakt, en nog een paar andere dingen … Maar verder?
Weinigen realiseren zich hoe belangrijk deze is voor de fysiologie en voor het leven: een goed functionerende pancreas is cruciaal voor optimale gezondheid en longevity.
Beste bezoeker, u heeft geen toegang.
Enkel (web)abonnees hebben toegang tot tijdschriftartikelen. Het webabonnement is nog in de maak.
U kunt zich wel alvast (gratis) registreren en tal van andere webartikelen raadplegen!
Auteur
Trefwoorden:
Verschenen in
Referenties
Lillycrop KA, Burdge GC. Epigenetic mechanisms linking early nutrition to long term health. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Oct;26(5):667-76.
Yajnik CS et al. Neonatal anthropometry: the thin-fat Indian baby. The Pune Maternal Nutrition Study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003 Feb;27(2):173-80.
Kulkarni ML, Mythri HP, Kulkarni AM. 'Thinfat' phenotype in newborns. Indian J Pediatr. 2009 Apr;76(4):369-73.
van Steijn L et al. Neonatal anthropometry: thin-fat phenotype in fourth to fifth generation South Asian neonates in Surinam. Int J Obes (Lond). 2009 Nov;33(11):1326-9.
Frantz ED, Peixoto-Silva N, Pinheiro-Mulder A. Endocrine pancreas development: effects of metabolic and intergenerational programming caused by a protein-restricted diet. Pancreas. 2012 Jan;41(1):1-9.
Martin-Gronert MS, Ozanne SE. Metabolic programming of insulin action and secretion. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14 S 3:29-39.
Lillycrop KA, Burdge GC. Epigenetic changes in early life and future risk of obesity. Int J Obes (Lond). 2011 Jan;35(1):72-83.
Sebert S, Sharkey D, Budge H, Symonds ME. The early programming of metabolic health: is epigenetic setting the missing link? Am J Clin Nutr. 2011 Dec;94(6 Suppl):1953S-1958S.
Theys N, Ahn MT, Bouckenooghe T, Reusens B, Remacle C. Maternal malnutrition programs pancreatic islet mitochondrial dysfunction in the adult offspring. J Nutr Biochem. 2011; 22(10):985-94.
Burdge GC et al. Epigenetic regulation of transcription: a mechanism for inducing variations in phenotype (fetal programming) by differences in nutrition during early life? Br J Nutr. 2007 Jun;97(6):1036-46.
Preidis GA et al. The Undernourished Neonatal Mouse Metabolome Reveals Evidence of Liver and Biliary Dysfunction, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress. J. Nutr. March 1, 2013 jn.113.183731
Tarry-Adkins JL, Chen JH, Jones RH, Smith NH, Ozanne SE. Poor maternal nutrition leads to alterations in oxidative stress, antioxidant defense capacity, and markers of fibrosis in rat islets: potential underlying mechanisms for development of the diabetic phenotype in later life. FASEB J. 2010; 24(8):2762-71.
Theys N, Bouckenooghe T, Ahn MT, Remacle C, Reusens B. Maternal low-protein diet alters pancreatic islet mitochondrial function in a sex-specific manner in the adult rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009; 297(5):R1516-25.
Chamson-Reig A, Thyssen SM, Arany E, Hill DJ. Altered pancreatic morphology in the offspring of pregnant rats given reduced dietary protein is time and gender specific. J Endocrinol. 2006 Oct;191(1):83-92.
Fowden AL, Hill DJ. Intra-uterine programming of the endocrine pancreas. Br Med Bull. 2001;60:123-42.
Heywood WE, Mian N, Milla PJ, Lindley KJ. Programming of defective rat pancreatic beta-cell function in offspring from mothers fed a low-protein diet during gestation and the suckling periods. Clin Sci (Lond). 2004 Jul;107(1):37-45.
Nys M. Spijsverteringsenzymen, miskend en onderschat, maar essentieel voor gezondheid en leven. AT&A 2012; 5:18-23.
Nys M. Probiotica en de darm: nieuwe gezichtspunten. AT&A 2011; 4:50-52.
Araújo TG et al. Hepatocyte growth factor plays a key role in insulin resistance-associated compensatory mechanisms. Endocrinology. 2012 Dec;153(12):5760-9.
Mellado-Gil J et al. Disruption of hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling enhances pancreatic beta-cell death and accelerates the onset of diabetes. Diabetes. 2011 Feb;60(2):525-36.
Pruimboom L. De lever/pancreas/resistenties binnen de klinische PNI. 2e jaar kPNI. 2011.
de Graaf-Roelfsema E. Glucose homeostasis and the enteroinsular axis in the horse: A possible role in equine metabolic syndrome. Vet J. 2013 Oct 4. pii: S1090-0233(13)00506-6.
Trivedi CD, Pitchumoni CS. Drug-induced pancreatitis: an update. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005 Sep;39(8):709-16.
Shachar E, Scapa E. Drug-induced pancreatitis. Harefuah. 2009 Feb;148(2):98-100, 139.
Douros A et al. Drug-induced acute pancreatitis: results from the hospitalbased Berlin case–control surveillance study of 102 cases. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2013; 38: 825–834
Badalov N, Baradarian R, Iswara K, Li J, Steinberg W, Tenner S. Drug-induced acute pancreatitis: an evidence-based review. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 Jun;5(6):648-61; quiz 644.
Vinklerová I, Procházka M, Procházka V, Urbánek K. Incidence, severity, and etiology of drug-induced acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2010 Oct;55(10):2977-81.
Bromer MQ, Black M. Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Clin Liver Dis. 2003 May;7(2):351-67.
Igarashi H, Ito T, Yoshinaga M, Oono T, Sakai H, Takayanagi R. Acetaminophen-induced acute pancreatitis. A case report. JOP. 2009 Sep 4;10(5):550-3.
Koulouris Z, Tierney MG, Jones G. Metabolic acidosis and coma following a severe acetaminophen overdose. Ann Pharmacother. 1999 Nov;33(11):1191-4.
Lochan R, Charnley RM, French JJ, Al-Mukhtar A, Hudson M, Manas DM, White SA. Successful management of necrotizing pancreatitis by percutaneous necrosectomy after orthotopic liver transplant for paracetamol induced acute liver failure: a case report. Exp Clin Transplant. 2009 Jun;7(2):110-4. Review.
Mietka-Ciszowska A, Stojakowska M, Groszek B. Severe paracetamol poisoning complicated with liver and renal failure--case report and review of literature. Przegl Lek. 2012;69(8):614-7.
Hodgman MJ, Garrard AR. A review of acetaminophen poisoning. Crit Care Clin. 2012 Oct;28(4):499-516.
Belhassen García M et al. Pancreatitis due to acetaminophen-codeine. An Med Interna. 2006 Aug;23(8):400-1.
Locher C, Lambare B, Fischer D, Labayle D. Acute pancreatitis induced by codeine-acetaminophen association: report of two cases. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2003 Jan;27(1):124-5.
Lederman JC, Nawaz H. Toxic interaction of didanosine and acetaminophen leading to severe hepatitis and pancreatitis: a case report and review of the literature. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001 Dec;96(12):3474-5.
Mogelijk verhoogd risico van pancreatitis en pancreaskanker door de antidiabetische geneesmiddelen die het incretine-effect versterken. http://www.bcfi.be/folia/index.cfm?FoliaWelk=F40N09F
Cohen D. Has pancreatic damage from glucagon suppressing diabetes drugs been underplayed? BMJ 2013;346:f3680
Potential harms of type 2 diabetes drugs have been ignored, finds BMJ investigation. BMJ 2013;346:f3782
Singh S et al. Glucagonlike Peptide 1–Based Therapies and Risk of Hospitalization for Acute Pancreatitis in Type 2 Diabetes MellitusA Population-Based Matched Case-Control Study. JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173(7):534-539.
Butler AE et al. Marked Expansion of Exocrine and Endocrine Pancreas with Incretin Therapy in Humans with increased Exocrine Pancreas Dysplasia and the potential for Glucagon-producing Neuroendocrine Tumors. Diabetes 013 March 22, doi: 10.2337/db12-1686
Brodovicz KG et al. Glucagon-like Peptide 1–Based Drugs and Pancreatic Safety. JAMA Intern Med.2013;173(19):1842-1843.
Gier B, Butler PC. Glucagonlike Peptide 1–Based Drugs and Pancreatitis: Clarity at Last, but What About Pancreatic Cancer? JAMA Intern Med. 2013;173(7):539-541.
Laczek JT, Shrestha M, Kortan ND, Lake JM. Carbamazepine-induced pancreatitis with positive rechallenge. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2010 Feb;44(2):153-4.
Becker C, Hvalic C, Delmore G, Krähenbühl S, Schlienger R. Recurrent acute pancreatitis during pravastatin-therapy. Praxis (Bern 1994). 2006 Jan 25;95(4):111-6.
Johnson JL, Loomis IB. A case of simvastatin-associated pancreatitis and review of statin-associated pancreatitis. Pharmacotherapy. 2006 Mar;26(3):414-22.
Singh S, Loke YK. Statins and pancreatitis: a systematic review of observational studies and spontaneous case reports. Drug Saf. 2006;29(12):1123-32.
Tsigrelis C, Pitchumoni CS. Pravastatin: a potential cause for acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Nov 21;12(43):7055-7.
Bai HX et al. Novel characterization of drug-associated pancreatitis in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011 Oct;53(4):423-8.
Sinclair DB, Berg M, Breault R. Valproic acid-induced pancreatitis in childhood epilepsy: case series and review. J Child Neurol. 2004 Jul;19(7):498-502.
Ozaydin E, Yükselgüngör H, Köse G. Acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis due to the use of valproic acid in a child. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2008 Mar;12(2):141-3.
Munhoz RP, dos Santos ML, Hernández-Fustes OJ. Fatal necro-hemorrhagic pancreatitis related to sodium valproate: case report. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2001 Sep;59(3-B):821-3.
Lenzen S. The mechanisms of alloxan- and streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia. 2008 Feb;51(2):216-26.
Dawud FA et al. Ameliorative Effects of Vitamin C and Zinc in Alloxan-induced Diabetes and Oxidative Stress in Wistar Rats. Curr Res Biolo Sc 2012; 4(2): 123-129.